where:
- PACKAGE_NAME is the name of the package.
- CLASS_NAME is the name of the class inside the package.
For example, we have another installed app in package "com.test.AndroidSlave", we can start the activity "com.test.AndroidSlave.AndroidSlaveActivity" inside the package.
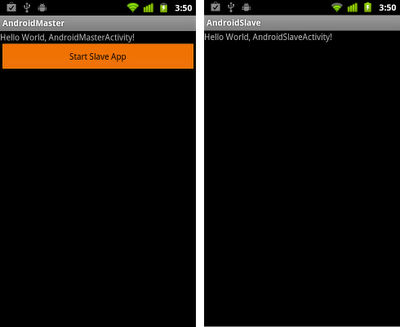
package com.test.AndroidMaster;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class AndroidMasterActivity extends Activity {
final static String PACKAGE_NAME = "com.test.AndroidSlave";
final static String CLASS_NAME = "com.test.AndroidSlave.AndroidSlaveActivity";
Button btnStartSlave;
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnStartSlave = (Button)findViewById(R.id.startalave);
btnStartSlave.setOnClickListener(new Button.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
startSlave();
}});
}
private void startSlave(){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClassName(PACKAGE_NAME, CLASS_NAME);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
Next post:
- Start a specified app with data passed
- Check if a app is instlled
Thanks for the simple explanation.
ReplyDelete